Selection Types
Selection types are the algorithms used in selection procedure.
Object raster selection methods are based on algorithms that analyze raster objects. The raster object may be interpreted in different ways:
Isolated raster object – raster area (contiguous set of raster dots);
Raster polyline segment – a part of raster line limited by endpoints or intersections with other objects;
Raster entity – a raster analogue of a vector entity: raster line, arc, and circle.
Most intellectual selection methods can manage all types of raster objects. When using those methods, specify the type of raster objects to be processed. The current selection type determines it.
There are three raster selection types.
| Selection type | Raster object type |
| Floodfilling | Isolated area on the raster image |
| Line Following | raster polyline segments |
| Object Type Recognition | raster entities |
Selecting Raster Object by Picking
The Object Type Recognition or Object method selects raster objects by picking. When selecting by picking, specify a point on image, and the program selects one raster object.
Object method is a basic one for all other object selection methods. Further, all of those methods can be represented as a combination of the standard selection method and the Object method.
This figure illustrates the result of selection by picking with the use of various selection types.
The raster objects selected are shown as outlines. In each of these three cases the picking point is defined in the centre of the horizontal raster line as shown in the figure on the left.








Selecting Isolated Raster Object
Picking on the raster using the Floodfilling type selects isolated raster areas. The program selects all raster dots connected to the point specified – these dots form contiguous set.
This method can be also treated as forced selection, since the type of selected object is predefined. See other methods of forced selection below in this chapter.
A set of raster dots is contiguous only if any dot belonging to the set is only adjacent to the dots of the same set. A contiguous set of image dots is surrounded by background dots that separates it from other objects in the image and makes it an isolated raster object.
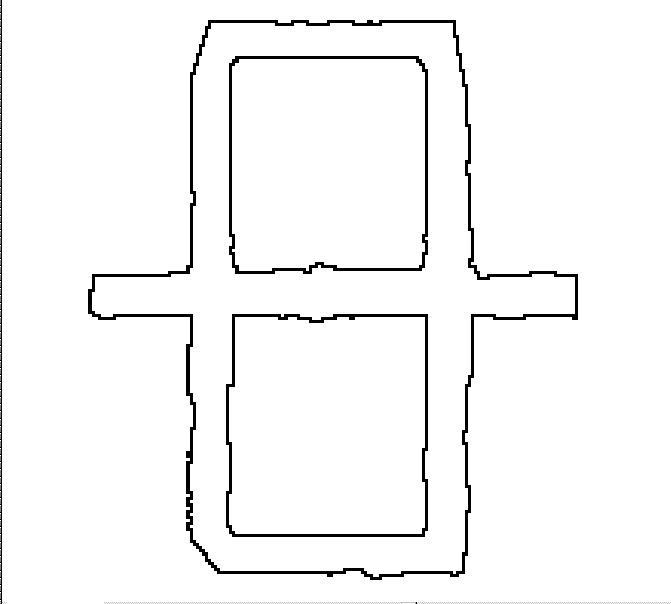
In this case the entire object is selected, as all its dots are contiguous.
This method is convenient when selecting standalone objects of arbitrary shape: characters, symbols, etc.









To select an area on the raster
 |
1. Click the button on the Select toolbar. 2. Click any point of the raster object. |
Selecting Raster Polyline Segments
Picking on the raster using the Line Following type selects an object called a raster polyline segment – sets of dots that look like line or arcs of approximately constant width, and with the length much greater than its width. The length of a raster object is the length of its centreline. The raster line shape is arbitrary.
After picking, the selection extends along the raster line from the specified point to a node of the raster line. A node of the raster line is either its endpoint, or a point where the line intersects with another raster object. So, using this method, a part of an arbitrary raster line bounded by two nodes of raster line can be selected – a raster polyline segment.
To distinguish raster lines from other raster objects the program uses the value of the maximal accepted raster line width. Objects of greater widths are not recognized as raster lines. A raster line may have breaks that should not be taken as endpoints. Define the value of the maximum break to be ignored. For description of Max Width and Max Break see Tuning Selection.
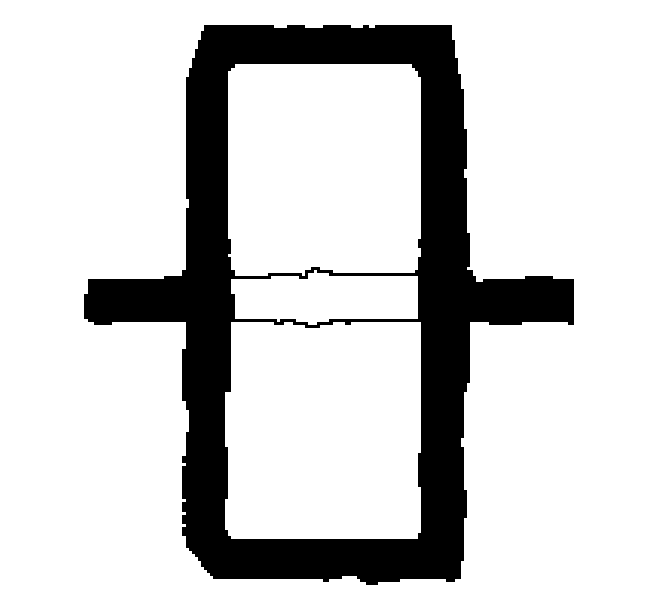
The figure shows that the program has selected part of the raster line until it meets the intersection with the other raster objects.










Selecting Raster Entities
Raster entities are raster objects shaped as basic vector objects – vector image entities. From here on we shall use the terms raster circle, raster arc, and raster line to imply raster objects that have a shape of a circle, arc, or line. However, note that real raster entities might have defects that hamper their identification by the program such as breaks, elliptical arcs and circles, varying width, etc.
If the Type Recognition selection is set, then the Object method can handle both raster lines and arbitrary raster objects with approximately equal width and length.
When a raster line is picked, the program identifies the type of a raster entity (line, arc or circle) and then tries to select the object of the most likely size. It ignores the points of intersection with other objects, and the selection extends until the symbol of the selected object becomes identical to the entity recognized. Since real raster objects may differ from ideal raster entities, the recognition tool uses the Approximation Accuracy parameter. This parameter defines the accepted level to which the real raster objects may differ from the ideal ones.
Selecting a raster entity preserves its intersections with other objects. Therefore, transforming and deleting raster data selected when Object Type Recognition is on does not create breaks in remaining raster objects. This allows the user to process raster data in the same manner as processing vector objects. For example, deleting a raster line that crosses the circle leaves the circle intact in the image, exactly as it happens when deleting a vector line that lies over a vector circle.
In case the raster object selected is not a raster line, the program detects its boundary and selects the object. An arbitrary raster object width should be greater than the maximum allowed width of a raster line.
To distinguish raster lines from other raster objects the program uses the reference value of the maximum accepted raster line width. For description of Approximation Accuracy, Max Width and Max Break see Tuning Selection.
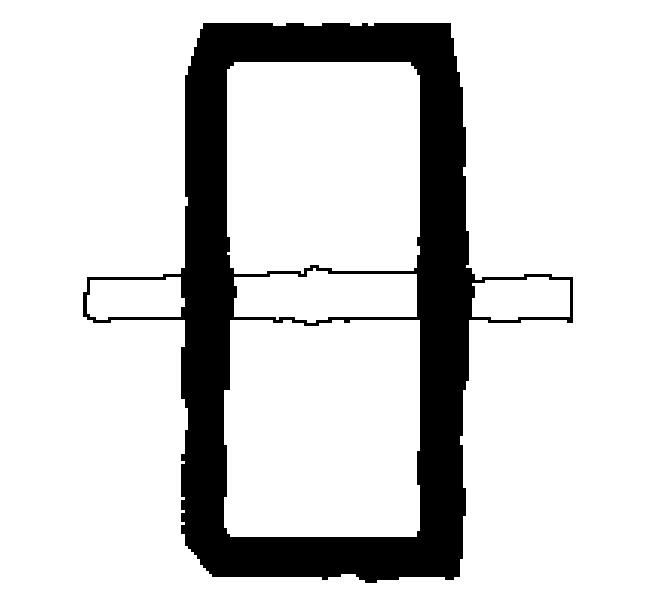
If selecting by picking with object recognition is on, then the program selects the entire raster line as shown with outlines on the left figure. Note that, when selecting, intersections of the selected line with other raster objects are not removed.









To select a raster entity
 |
1. Click the Auto button on the Raster Select toolbar. 2. Click a point on the raster image. |




Post your comment on this topic.